What are Cannabinoids?
Before we dive into what Cannabinoids are, I want you to think back for just a second and remember when you were younger and your elders told you to eat your veggies or drink your orange juice for the vitamin C to fight off the flu. Our diet is absolutely critical in how we feel, how healthy we are and even how long we live because our diet is where the vitamins and nutrients come from.
That special person popped into your head didn’t they, yeah mine was my mom and grandmother. We all know the fact that our health is greatly impacted by our diet, affecting the health of our body and mind. Cannabinoids play as much if not more of a role in the picture of our health and well-being. Below are just a few examples.

Now Lets Talk about Cannabinoids?
There are more than 113 different chemical compounds identified in both the hemp and Marijuana plant, CBD and THC are the two most abundant and well known of the many cannabinoids found in cannabis. Their chemical makeups are similar to the endocannabinoids that our body makes naturally, which allows them to interact with the Endocannabinoid System’s cannabinoid receptors to alter the release of neurotransmitters in the brain. They are similar in many ways and can be found in the seeds, stalks, and flowers of both hemp and marijuana, but in very different – and critical – ratios.
In Marijuana that has been cultivated for decades for the euphoric & intoxicating effects, THC can be found in concentrations ranging from 3-12 percent, with CBD as low as .01%. To be federally acceptable, hemp’s chemical composition of THC must be no greater than 0.3%, nearly 10 times less than the least potent strain of marijuana. This not only means that CBD can never cause a high, no matter how much is consumed (this has recently been debated), but that it can counteract the binding effects of the THC with the CB1 receptors.
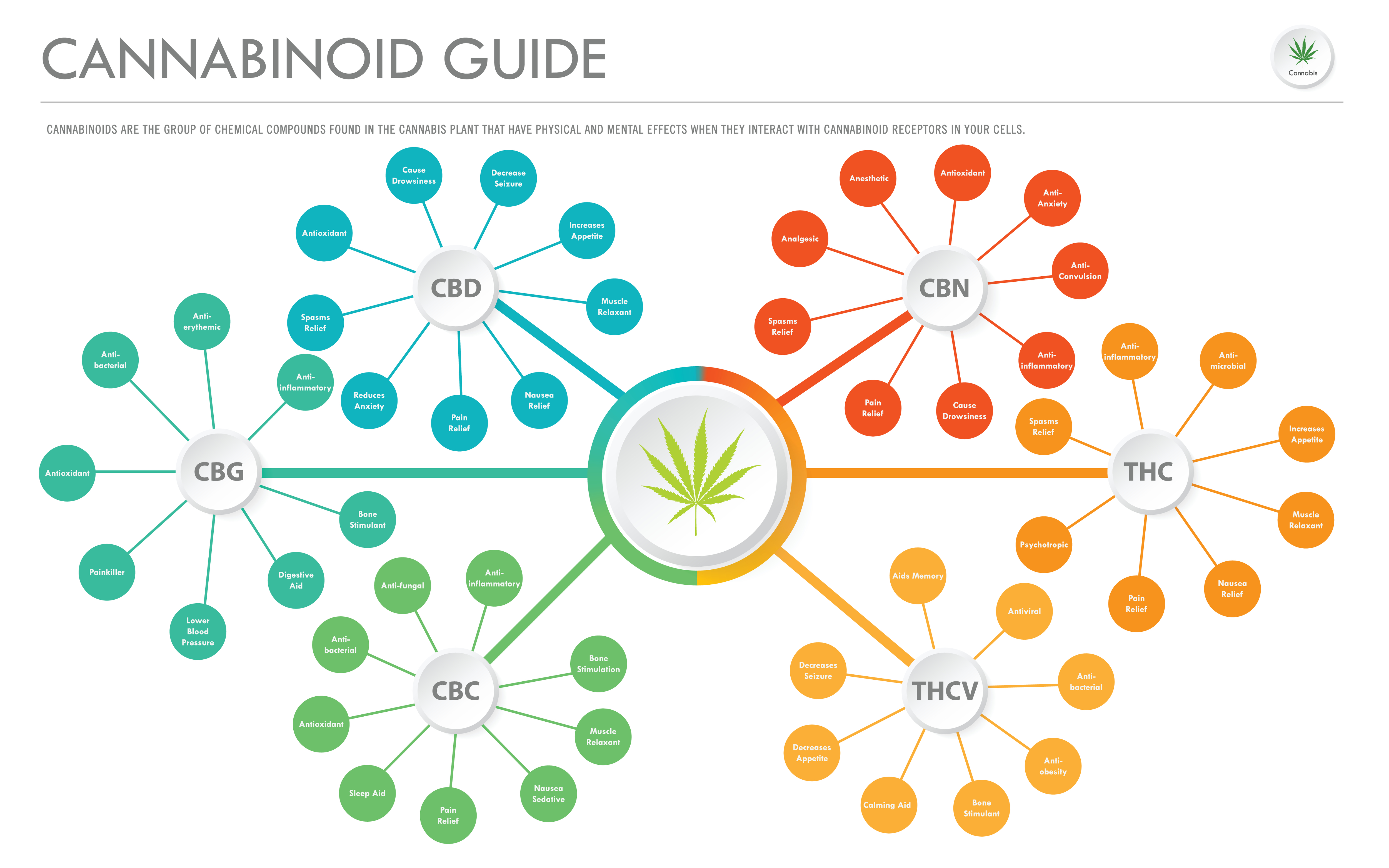
CB1 receptors are found mostly in the central nervous system. CB2 receptors, on the other hand, are found throughout the body, in the vital organs, peripheral muscles, and reproductive organs. They both interact with the endocannabinoid system but elicit different natural effects.
CBD and THC both interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system and its specialized cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2. It is through these interactions that these two cannabinoids augment the endocannabinoid system and encourage balance. However, the ways in which the two cannabinoids interact with these cannabinoid receptors vary.
THC directly binds with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, while having a higher affinity for CB1 receptors. CBD, on the other hand, has little affinity for the two cannabinoid receptors. Instead, it acts as an indirect antagonist of cannabinoid agonists. This means that CBD acts to suppress the CB1 and CB2 activating qualities of a cannabinoid-like THC. CBD has also been found to interact with other non-cannabinoid receptors, including 5-HT1A receptors and the vanilloid receptor TRPV-1.
Why all the differences? Technically speaking both chemicals are isomers; they share the same chemical composition C21H30O2 but their atomic arrangements differ. Both CBD and THC are considered cyclic compounds, which means one or more series of atoms in the compounds are connected to form a ring. CBD comes with an open ring with a hydroxyl and alkene group, while THC supports a closed ring with an ester group.
Popular Cannabinoids
Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA)
Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA)
Cannabinol (CBN)
Cannabinol (CBN)
Cannabigerol (CBG)
Cannabigerol (CBG)
Cannabichromene (CBC)
Cannabichromene (CBC)
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)
Cannabidivarin (CBDV)
Cannabidivarin (CBDV)
What are Terpenes & What Do They Do?
Terpenes are the organic compounds responsible for creating the unique aroma of each individual cannabis plant.
When terpenes work together with cannabinoids, in a process known as the entourage effect, the therapeutic potentials increase dramatically.
Terpenes can also modify how much of each cannabinoid is absorbed.
Hover over the Terpene guide with your mouse.

By now you have probably figured out there’s a lot of really cool natural remedies that God put on this Earth for us to find. Ready for the best part, The ECS!!